Researchers in St. Louis have launched a study into whether a long-used antidepressant can reduce the likelihood that COVID-19 will turn deadly.
Can an antidepressant stop COVID-19’s deadly ‘cytokine storm’? (Links to an external site)


Researchers in St. Louis have launched a study into whether a long-used antidepressant can reduce the likelihood that COVID-19 will turn deadly.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine are recruiting COVID-19 patients for a clinical trial that will examine whether an existing anti-depressant can be an effective treatment for COVID-19.

Washington University in St. Louis will begin construction in March on what will be one of the largest neuroscience research buildings in the country.

Neuroactive steroid drugs result from Taylor Family Institute, pharma collaboration
Glowinski, artist Outlaw address mental health through artwork.

Philanthropists Andrew and Barbara Taylor and the Crawford Taylor Foundation have committed $10 million to Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis to continue research to investigate the scientific underpinnings of psychiatric illnesses, with the goal of improving diagnosis and treatment.

Adult depression has long been associated with shrinkage of the hippocampus, a brain region that plays an important role in memory and response to stress. Now, new research from Washington University in St. Louis has linked participation in team sports to larger hippocampal volumes in children and less depression in boys ages 9 to 11.

A biomedical engineer at Washington University in St. Louis is developing a therapeutic option that would prevent the opiates from crossing the blood-brain barrier, preventing the high abusers seek.
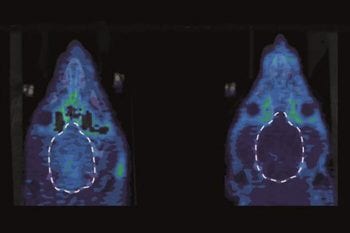
Blocking a type of opioid receptor restores motivation

Study refutes idea that children who talk about suicide don’t understand it

Seven years ago, Chancellor Mark S. Wrighton (left) asked Andrew C. Taylor, executive chairman of Enterprise Holdings and a life trustee of the university, to chair the public phase of Leading Together.

Also Known As: δ* KI δ* KI is a CRISPR/cas9-made knock-in allele with a T269Y mutation in Gabrd exon 8 that renders δ-containing receptor populations insensitive to picrotoxin (PTX). These mice allow chemogenetic isolation of δ-containing GABAA receptors, and may be useful for neurological studies of receptor, ion channel and synapse biology, neurotransmitters, and glutamate/GABA transmission.
Brain changes evident in scans before memory, cognitive decline

In 2012, Andrew and Barbara Taylor and the Crawford Taylor Foundation pledged $20 million to the Department of Psychiatry at Washington University’s School of Medicine to establish a research institute dedicated to advancing new treatments for mental illnesses. Just six years later, investigators in the department’s Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research are on […]
Parent-child interactive therapy decreases depressive symptoms in kids.
A national study led by institute affiliate Charles Conway, MD, indicates that people treated with nerve stimulation experience significant improvements in quality of life, even when their depression symptoms don’t completely dissipate.

In the new research, Steve Mennerick, Institute scientific director, and his colleagues focused on GABA receptors located on neurons in the brain’s hippocampus, a part of the brain involved in learning and memory. Using CRISPR, they mutated the delta-type GABA receptors to isolate and test their role in brain functioning.
Nitrous oxide, or laughing gas, has shown early promise as a potential treatment for severe depression in patients whose symptoms don’t respond to standard therapies. The pilot study was believed to be the first research in which patients with depression were given laughing gas.